In the oil and gas industry, valves play a critical role in ensuring the safe and efficient flow of natural resources. From extraction to distribution, various types of valves are employed to control, isolate, and direct the flow of oil and gas. Understanding the types of valves used, as well as their specific applications, is crucial for anyone involved in this industry. This blog will delve into the most common valves used in oil and gas operations, their functions, and why they are essential.

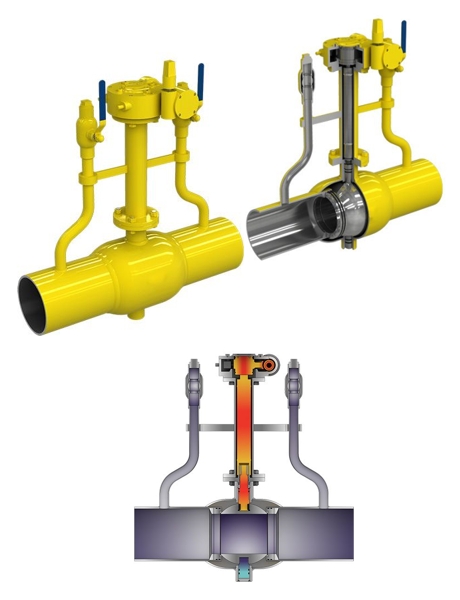
One of the most widely used valve types in the oil and gas industry is the ball valve. Ball valves utilize a spherical perforated obstruction (known as a rotary ball) to stop and start the hydraulic flow. This valve is typically rotated 90 degrees around its axis (a quarter-turn) to open or close, making it a quick and reliable option for controlling fluid flow.
Ball valves are suitable for both liquid and gas services, and they are particularly popular in the chemical, petrochemical, and oil and gas industries. Their long service life and reliable sealing capabilities make them ideal for use in harsh environments, including vacuum and cryogenic services. While they are sometimes used as control valves due to their cost-effectiveness, they are not preferred for precise control because they don’t allow for fine adjustments.
In the context of gas and oil production, ball valves are commonly found in subsea isolation and shut-down facilities, oil-head isolation, pipeline surge control, processing separation, storage, transmission and distribution, as well as secondary and enhanced oil recovery.
Fully welded ball valve is a type of ball valve characterized by its construction, where the body of the valve is entirely welded, without any bolted connections or flanges. This design eliminates potential leak paths and provides a hermetically sealed system, enhancing the valve's durability and reliability. These valves are especially suited for high-pressure applications and are commonly used in pipelines that transport oil and gas over long distances. The fully welded construction ensures there are no leak paths, making them ideal for underground and subsea applications.
Gate valves are another essential component in the oil and gas industry. These valves operate by lifting a gate out of the path of the fluid. When the gate is fully lifted, the flow is unobstructed; when it is lowered, the flow is stopped. Gate valves are typically used when a straight-line flow of fluid and minimal restriction is desired.
These valves are not ideal for regulating flow, as they are designed to be either fully open or fully closed. Their primary advantage lies in their ability to provide a tight seal, which is crucial in oil and gas pipelines to prevent leakage.
Unlike gate valves, globe valves are designed for regulating flow. They consist of a movable disk-type element and a stationary ring seat in a generally spherical body. Globe valves are particularly useful in applications where flow needs to be controlled or throttled.
In the oil and gas industry, globe valves are often used in applications where pressure drop is not a major concern. They are ideal for systems where flow control is necessary, such as in fuel oil systems and cooling water systems.
Check valves are designed to allow fluid to flow in one direction only, preventing backflow that could cause damage to the system. They are commonly used in oil and gas pipelines to protect equipment from damage due to reverse flow.
In the oil and gas sector, check valves are often installed at the discharge side of pumps, where they ensure that the fluid flows in the intended direction only. They are a vital safety component, preventing accidents and ensuring the smooth operation of pipelines.
Butterfly valves are quarter-turn valves like ball valves, but they use a disk instead of a ball to regulate flow. These valves are lightweight, cost-effective, and can be used in a variety of applications, including those in the oil and gas industry.
Butterfly valves are especially useful in large-diameter pipelines where space is limited. They are commonly employed in systems where quick shut-off is required. However, they are generally not used in high-pressure applications due to their lower pressure resistance compared to ball and gate valves.
Plug valves are a type of valve that uses a cylindrical or conically tapered plug to control the flow of fluid. The plug has one or more hollow passageways that allow fluid to flow through when aligned with the inlet and outlet ports. By rotating the plug, the flow can be blocked or allowed to pass, similar to the operation of a ball valve.
Plug valves are commonly used in the oil and gas industry because of their robust design and ability to handle high pressures and abrasive fluids. They are particularly well-suited for applications that require a simple on/off function, such as in pipelines, gas processing, and storage facilities. The design of plug valves allows for quick operation and reliable sealing, which is critical in isolating sections of a pipeline or processing system.
Slam-shut valves are specialized safety devices designed to automatically shut off the flow of gas or liquid in the event of a system failure or abnormal operating condition. These valves are often used in conjunction with pressure regulators in gas distribution systems. If the system detects a pressure that is too high or too low, the slam-shut valve will quickly close to prevent potential hazards, such as explosions or equipment damage.
In the oil and gas industry, slam-shut valves are essential for ensuring safety in high-risk environments. They are commonly used in gas distribution networks, upstream production facilities, and processing plants where the automatic shutdown of flow is crucial to preventing accidents.
Needle valves are used for precise control of flow in small-diameter piping systems. They feature a small, tapered needle-like plunger that can be screwed in or out to vary the flow rate. Needle valves are typically used in applications where fine adjustments are necessary, such as in measuring instruments, sampling lines, and small-diameter pipelines.
In the oil and gas industry, needle valves are often found in instrumentation systems where they provide precise control over the flow of gas or liquid. Their ability to finely adjust flow makes them ideal for applications requiring accurate flow regulation.
Choke valves are designed to control the flow of fluids by varying the flow area. These valves are commonly used in oil and gas production, particularly in wellhead assemblies. Choke valves help regulate the flow rate from a well, which is critical for controlling pressure and ensuring the safe production of hydrocarbons.
There are two main types of choke valves: adjustable chokes and positive chokes. Adjustable chokes allow for manual or automatic adjustment of the flow area, while positive chokes have a fixed flow area. Choke valves play a vital role in maintaining the desired flow rate and pressure in oil and gas production systems.
Pressure relief valves are safety devices that automatically release pressure from a system when it exceeds a predetermined level. These valves are crucial in preventing overpressure conditions that could lead to equipment failure or catastrophic events, such as explosions.
In the oil and gas industry, pressure relief valves are used in a variety of applications, including pipelines, processing equipment, and storage tanks. They ensure that the pressure within a system remains within safe limits, protecting both the equipment and personnel.
Valves are indispensable components in the oil and gas industry, providing critical control over the flow of resources from extraction to distribution. The type of valve used depends on the specific requirements of the system, including factors like pressure, flow control, and safety considerations. Ball valves, gate valves, globe valves, check valves, and butterfly valves all have unique roles in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of oil and gas pipelines. Understanding the functions and applications of these valves is essential for maintaining the integrity and safety of the oil and gas infrastructure.
The oil and gas industry relies on a wide range of valves to ensure safe and efficient operations. Plug valves and slam-shut valves are just two examples of the specialized equipment used to manage the flow of hydrocarbons and protect infrastructure from potential hazards. Along with other valves such as needle valves, choke valves, and pressure relief valves, these components are integral to maintaining the safety, reliability, and efficiency of oil and gas operations.
Understanding the unique functions and applications of each valve type is essential for anyone involved in the design, operation, or maintenance of oil and gas facilities. By selecting the right valve for each application, operators can ensure the smooth and safe operation of their systems, ultimately contributing to the success of their operations.
As a global leading valve manufacturer, we would be pleased to advise you individually, and you are also welcome to send your inquiry to us ( [email protected] ).